Solid-State Batteries: US Research Promises 25% Longer EV Range by Mid-2025

Pioneering US research is advancing solid-state battery technology, projecting a significant 25% increase in electric vehicle range by mid-2025, signaling a transformative shift in EV capabilities and widespread adoption.
The future of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly approaching a significant milestone, with new US research indicating that solid-state battery research could deliver a remarkable 25% longer range for future EVs by mid-2025. This advancement promises to redefine what we expect from electric transportation, addressing range anxiety and accelerating EV adoption nationwide.
Understanding Solid-State Battery Technology
Solid-state batteries represent a revolutionary leap from traditional lithium-ion batteries. Instead of a liquid or gel electrolyte, these batteries utilize a solid material, offering several compelling advantages that could transform the electric vehicle landscape.
This fundamental change in composition addresses many of the limitations associated with current EV battery technology, paving the way for safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting power sources. The shift to solid electrolytes is not merely an incremental improvement; it is a foundational change with far-reaching implications for performance and safety.
The Core Difference: Solid Electrolyte
The primary distinction of solid-state batteries lies in their electrolyte. While conventional lithium-ion batteries use a flammable liquid electrolyte, solid-state batteries employ a non-flammable solid material. This solid material can be ceramic, glass, or a polymer, each with unique properties being explored by researchers.
- Enhanced Safety: Eliminates the risk of thermal runaway and fires associated with liquid electrolytes.
- Higher Energy Density: Allows for more energy storage in a smaller, lighter package.
- Improved Durability: Less prone to degradation over time, leading to longer battery life.
- Faster Charging: Potential for significantly reduced charging times due to stable ion transfer.
The implications of a solid electrolyte extend beyond safety. The ability to pack more energy into a smaller volume means vehicles can travel further on a single charge, or manufacturers can design lighter vehicles with the same range. This improved energy density is a critical factor in extending EV range and enhancing overall vehicle performance.
In essence, solid-state battery technology promises to deliver a safer, more robust, and more powerful energy storage solution for electric vehicles. The ongoing research and development in this field are crucial for realizing the full potential of electric transportation.
US Research Breakthroughs and Their Impact
The United States is at the forefront of solid-state battery research, with numerous academic institutions, government labs, and private companies dedicating substantial resources to accelerate development. These breakthroughs are not just theoretical; they are translating into tangible advancements that promise to reshape the EV market.
Recent findings from leading research institutions highlight significant progress in material science and engineering, pushing the boundaries of what was previously thought possible. These advancements are critical for overcoming the remaining challenges in bringing solid-state batteries to commercial viability.
Key Institutions and Innovations
Several prominent US entities are driving the innovation in solid-state battery technology. Their collaborative efforts are creating a robust ecosystem for rapid progress.
- National Labs: Laboratories such as Argonne and Pacific Northwest are pioneering new material discoveries and characterization techniques.
- University Research: Institutions like Stanford, MIT, and UC Berkeley are exploring novel solid electrolyte compositions and manufacturing processes.
- Private Sector Investment: Companies like QuantumScape, Solid Power, and others are scaling up production and refining their proprietary technologies.
These organizations are focusing on various aspects of solid-state battery development, from fundamental material science to advanced manufacturing techniques. The diversity of approaches ensures that multiple pathways to commercialization are being explored simultaneously, increasing the likelihood of success.
The collective impact of these US-led research efforts is profound. By addressing the core technical hurdles, these institutions are not only improving battery performance but also laying the groundwork for a sustainable and efficient energy future. The focus on practical applications means that these breakthroughs are designed with future EVs in mind.
Projected 25% Longer Range by Mid-2025
One of the most exciting outcomes of the latest US research is the projection of a 25% increase in EV range by mid-2025, directly attributable to solid-state battery integration. This isn’t merely an optimistic forecast; it’s a target backed by concrete progress in energy density and efficiency.
Achieving this substantial range improvement would significantly enhance the appeal of electric vehicles, making them a more viable option for a wider segment of consumers. The ability to travel further on a single charge directly tackles one of the primary concerns for potential EV buyers: range anxiety.
How a 25% Increase Translates to Real-World Driving
A 25% increase in range means an EV that currently travels 300 miles on a charge could extend that to 375 miles. This improvement is substantial, offering greater flexibility and confidence for long-distance travel.
- Reduced Charging Stops: Fewer interruptions on road trips, making travel more convenient.
- Greater Daily Utility: More usable range for daily commutes and errands without constant recharging.
- Competitive Edge: EVs become even more competitive with gasoline-powered vehicles in terms of travel capacity.
This enhanced range also opens up new possibilities for vehicle design and usage. Manufacturers could potentially offer smaller, lighter battery packs that still provide ample range, reducing vehicle weight and improving overall efficiency. Alternatively, they could maintain current battery sizes and offer a significant boost in travel distance.
The projected timeline of mid-2025 suggests that these advancements are not far off. This rapid development underscores the intensity and success of current research efforts, positioning solid-state batteries as a near-term solution for boosting EV performance. The real-world implications for drivers are substantial, promising a more seamless and enjoyable EV experience.
Overcoming Challenges in Solid-State Battery Production
While the promise of solid-state batteries is immense, their mass production presents a unique set of challenges that researchers and manufacturers are diligently working to overcome. Scaling up from laboratory prototypes to commercial volumes requires addressing complex engineering and material science hurdles.
These challenges include finding cost-effective manufacturing methods, ensuring material compatibility, and developing robust quality control processes. The success of solid-state batteries hinges on effectively navigating these production complexities.
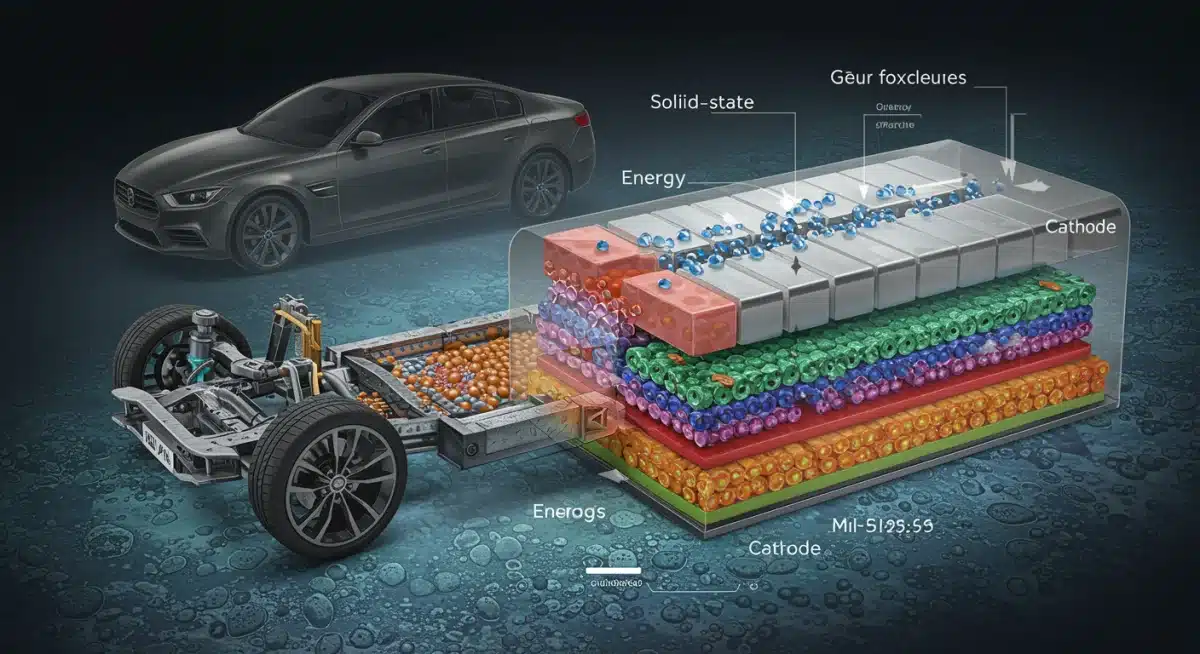
Key Production Hurdles
The path to widespread solid-state battery adoption involves tackling several technical and economic obstacles. Each hurdle requires innovative solutions and significant investment.
- Material Costs: Some solid electrolyte materials can be expensive to produce at scale.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Processes for creating thin, uniform solid electrolyte layers are intricate.
- Interface Stability: Ensuring stable contact between the solid electrolyte and electrodes is critical for performance.
- Thermal Management: Developing effective cooling systems for solid-state batteries, despite their inherent stability.
Addressing these issues involves a multi-pronged approach, combining advanced material science with sophisticated engineering techniques. Researchers are exploring new material compositions that are both high-performing and cost-effective, while engineers are developing novel manufacturing processes that can be scaled efficiently.
Despite these challenges, the progress being made is encouraging. Innovations in deposition techniques and assembly processes are steadily bringing down production costs and improving reliability. The collaborative efforts between academia and industry are crucial in accelerating the transition from lab-scale success to commercial viability.
The Economic and Environmental Benefits
The widespread adoption of solid-state batteries, fueled by US research, promises significant economic and environmental benefits. Beyond extended range, these batteries offer a cleaner, more sustainable, and economically viable future for electric transportation.
The improvements in efficiency and safety contribute to a lower overall cost of ownership for EVs, while their environmental footprint is considerably reduced compared to traditional vehicles. This dual benefit makes solid-state batteries a powerful catalyst for change.
Driving Towards Sustainability and Cost Efficiency
The advantages of solid-state technology extend far beyond individual vehicle performance, impacting broader economic and ecological systems.
- Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Accelerates the shift away from gasoline, enhancing energy independence.
- Lower Carbon Emissions: Contributes significantly to global efforts to combat climate change.
- Longer Lifespan: Less frequent battery replacement reduces waste and resource consumption.
- Potential for Recycling: Solid components may simplify recycling processes compared to liquid electrolytes.
- Lower Operating Costs: More efficient energy storage can lead to cheaper electricity consumption per mile.
The economic benefits are not limited to consumers. Industries involved in battery manufacturing, EV production, and charging infrastructure stand to gain from increased demand and technological advancements. This growth can create new jobs and stimulate economic development in the clean energy sector.
Environmentally, the shift to solid-state batteries supports a circular economy model. Their enhanced durability and potential for easier recycling mean a reduction in raw material extraction and waste generation. This comprehensive approach to sustainability makes solid-state batteries a cornerstone of future green initiatives.
Future Outlook and Commercialization Timeline
The path to full commercialization for solid-state batteries is becoming clearer, with mid-2025 marking a crucial inflection point for significant range improvements. While mass market adoption will take longer, initial deployments in premium EVs and specialized applications could arrive sooner.
The rapid pace of innovation and investment suggests that solid-state technology is on track to become a mainstream component of electric vehicles within the next decade. The groundwork laid by current US research is accelerating this timeline considerably.
Key Milestones and Projections
Several key indicators suggest a promising future for solid-state batteries, with various stages of deployment anticipated.
- Mid-2025: Expected debut of vehicles with solid-state components offering a 25% range increase, likely in limited production or high-end models.
- Late 2020s: Broader integration into a wider range of EV models as production scales and costs decrease.
- Early 2030s: Potential for solid-state batteries to become the dominant battery technology in new EVs.
- Continued Innovation: Ongoing research will focus on further increasing energy density, reducing costs, and improving charging speeds beyond current projections.
The collaborative efforts between automakers and battery developers are crucial for meeting these timelines. Partnerships are forming to co-develop and integrate solid-state technology into future vehicle platforms, ensuring seamless adoption. This integration involves not just the battery itself, but also the vehicle’s entire energy management system.
Ultimately, the future outlook for solid-state batteries is exceptionally bright. With continued investment and research, these advanced power sources are poised to make electric vehicles even more attractive, efficient, and environmentally friendly, fundamentally changing the automotive landscape for generations to come.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 25% Longer EV Range | US research projects a significant increase in electric vehicle range by mid-2025 thanks to solid-state batteries. |
| Solid-State Technology | Utilizes a solid electrolyte, enhancing safety, energy density, and durability compared to liquid-ion batteries. |
| US Research Leadership | National labs, universities, and private companies are driving innovation and overcoming production challenges. |
| Commercialization Timeline | Initial deployments expected by mid-2025, with broader adoption in the late 2020s and early 2030s. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries use a non-flammable solid electrolyte instead of the liquid electrolyte found in traditional lithium-ion batteries. This eliminates the risk of thermal runaway and associated fires, significantly enhancing the safety profile of electric vehicles.
A 25% range increase means EVs can travel significantly further on a single charge. For example, a 300-mile range car could go 375 miles. This reduces range anxiety, minimizes charging stops, and makes long-distance travel much more convenient for drivers.
US research indicates that initial deployments of solid-state battery technology, offering a 25% range increase, could appear in some EV models by mid-2025. Broader commercialization and widespread adoption are projected for the late 2020s and early 2030s.
Yes, solid-state batteries offer several environmental benefits. Their longer lifespan reduces the need for frequent replacements, and the solid components may simplify recycling processes. They also contribute to lower carbon emissions by enabling more efficient electric transportation.
Key challenges include high material costs, complex manufacturing processes for thin solid electrolyte layers, ensuring stable interfaces between components, and developing efficient thermal management systems. Researchers are actively working to overcome these hurdles for scalable production.
Conclusion
The latest US research into solid-state battery technology marks a pivotal moment for the electric vehicle industry. With projections indicating a 25% increase in EV range by mid-2025, the long-standing concerns around range anxiety are being systematically addressed. These advancements promise not only enhanced performance and safety but also significant economic and environmental benefits, accelerating the global transition to sustainable transportation. The collaborative efforts across national labs, universities, and private enterprises are paving the way for a future where electric vehicles are more accessible, efficient, and integral to our daily lives than ever before.





