Automotive Workforce Future: Bridging the U.S. Skill Gap by 2025
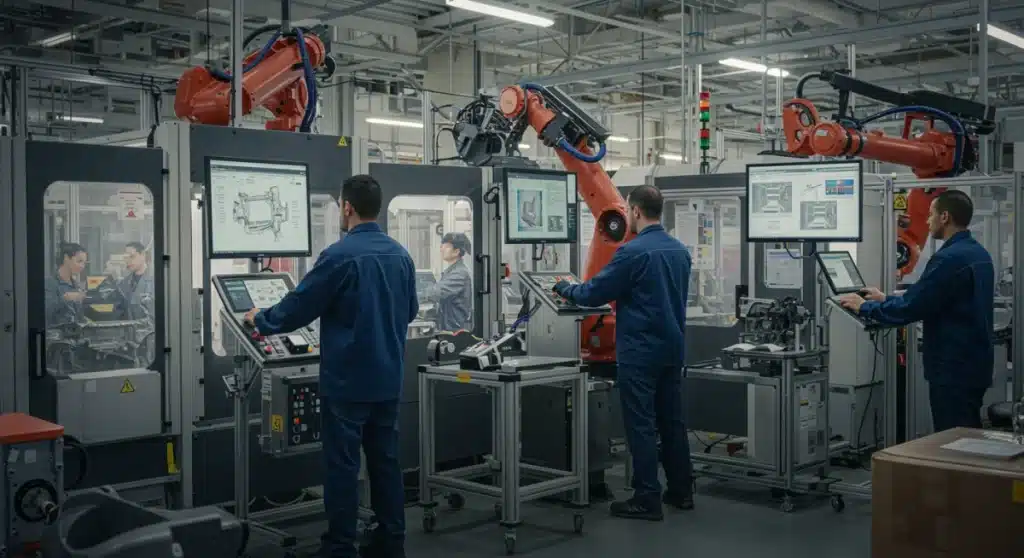
U.S. automotive manufacturers are actively implementing comprehensive strategies, including advanced training and technology integration, to effectively address a projected 8% skill gap in their workforce by 2025, ensuring industry resilience and innovation.
The landscape of the automotive industry is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements, electrification, and automation. This evolution presents both immense opportunities and significant challenges, particularly concerning the workforce. One of the most pressing concerns for U.S. manufacturers is the future of automotive workforces: How U.S. manufacturers are addressing a projected 8% skill gap by 2025. This anticipated gap underscores the urgent need for strategic interventions to ensure a skilled and adaptable labor force capable of navigating the complexities of modern vehicle production.
Understanding the Automotive Skill Gap Challenge
The U.S. automotive industry, a cornerstone of the nation’s economy, faces a critical juncture. The rapid pace of innovation, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving, and advanced manufacturing processes, has created a mismatch between the skills workers currently possess and those required for future roles. This skill gap is not merely a theoretical concern; it represents a tangible threat to production efficiency, innovation, and global competitiveness.
This challenge extends beyond traditional manufacturing roles. It impacts engineers, technicians, software developers, and even supply chain managers. The shift from internal combustion engines to electric powertrains, for instance, demands a completely new set of expertise in areas like battery technology, power electronics, and charging infrastructure. Manufacturers must adapt quickly, or risk falling behind.
Technological Shifts Driving the Gap
The advent of industry 4.0 technologies has profoundly reshaped manufacturing. Automation, AI, and data analytics are no longer futuristic concepts but integral components of modern production lines. Workers need to be proficient in:
- Operating and maintaining advanced robotics and automated systems.
- Interpreting and utilizing data from production processes for optimization.
- Troubleshooting complex software and hardware integrations.
These skills are often not covered in traditional vocational training programs, leading to a deficit in the available talent pool. The demand for these specialized competencies is growing exponentially, further widening the existing gap.
Strategic Initiatives for Workforce Development
U.S. automotive manufacturers are not passively observing this trend; they are actively implementing comprehensive strategies to mitigate the skill gap. These initiatives are multifaceted, encompassing education, training, and recruitment, all aimed at building a resilient and future-proof workforce. The goal is to not only fill the current vacancies but also to prepare employees for the roles that haven’t even been conceived yet.
Collaboration is key in these efforts, with manufacturers partnering with educational institutions, government agencies, and industry associations. This collaborative ecosystem ensures that training programs are relevant, accessible, and aligned with industry needs. Such partnerships are crucial for developing standardized curricula and certifications that are recognized across the industry.
Investing in Upskilling and Reskilling Programs
One of the most effective ways to address the skill gap is through robust internal training programs. Companies are investing heavily in upskilling their current employees, equipping them with the new competencies required for evolving roles. Reskilling initiatives, on the other hand, focus on transitioning workers from declining roles into new, high-demand positions.
- On-the-job training: Practical experience combined with theoretical knowledge.
- Apprenticeships: Structured programs blending work experience with classroom instruction.
- Certification programs: Industry-recognized credentials for specialized skills.
These programs often leverage virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) for immersive training experiences, allowing employees to practice complex tasks in a safe and controlled environment. This hands-on approach accelerates learning and improves retention.
Academia and Industry Partnerships
The synergy between educational institutions and the automotive industry is vital. Universities, community colleges, and vocational schools are adapting their curricula to meet the specific needs of modern manufacturing. This includes developing new degree programs, certifications, and workshops focused on emerging technologies.
Manufacturers are actively engaging with these institutions, providing input on curriculum design, offering internships, and even donating equipment. This ensures that graduates are job-ready upon entering the workforce, possessing the practical skills and theoretical knowledge demanded by the industry. These partnerships also foster research and development, pushing the boundaries of automotive innovation.
Bridging the Gap Through STEM Education
A long-term solution involves strengthening STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education at all levels, from K-12 to higher education. Encouraging students to pursue careers in these fields is fundamental to building a robust talent pipeline for the future.
- Early STEM exposure: Introducing robotics and coding in elementary schools.
- Mentorship programs: Connecting students with industry professionals.
- Scholarships and grants: Supporting students pursuing automotive-related studies.
By investing in STEM education, manufacturers are not only addressing the immediate skill gap but also cultivating a generation of innovators who will drive the industry forward. This proactive approach ensures a sustainable supply of skilled workers for decades to come.
Leveraging Automation and AI for Efficiency
While automation and artificial intelligence are often cited as drivers of the skill gap, they also present powerful solutions. By automating repetitive and hazardous tasks, manufacturers can free up human workers to focus on more complex, value-added activities that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. This shift necessitates a new set of skills, but it also enhances overall efficiency and safety.
AI-powered tools can also assist in workforce planning, identifying skill gaps, and recommending personalized training paths for employees. Predictive analytics can forecast future skill demands, allowing manufacturers to proactively develop training programs. This intelligent approach to workforce management optimizes resource allocation and ensures a highly adaptive labor force.

Human-Robot Collaboration
The future of automotive manufacturing is not about replacing humans with robots, but rather about fostering human-robot collaboration (cobots). Cobots are designed to work alongside humans, augmenting their capabilities and improving productivity. This requires workers to understand how to interact with and program these intelligent machines.
Training programs are increasingly focusing on human-robot interface, teaching employees how to program, supervise, and troubleshoot cobots. This blend of human ingenuity and robotic precision creates a more efficient and flexible production environment. It also elevates the roles of human workers, moving them from manual labor to supervisory and analytical positions.
Attracting and Retaining New Talent
Beyond training the existing workforce, manufacturers must also focus on attracting new talent to the industry. The perception of manufacturing jobs needs to evolve from labor-intensive and repetitive to technologically advanced and innovative. This requires a concerted effort to showcase the exciting career opportunities available in modern automotive production.
Retention is equally crucial. High turnover rates can exacerbate the skill gap and lead to significant operational costs. Companies are implementing various strategies to improve employee satisfaction and loyalty, including competitive compensation, professional development opportunities, and a positive work culture. A supportive environment encourages continuous learning and growth, making employees feel valued.
Promoting Diversity and Inclusion
A diverse and inclusive workforce brings a wider range of perspectives and skills, fostering innovation and problem-solving. Manufacturers are actively working to attract individuals from underrepresented groups, including women, minorities, and veterans, to the automotive sector. This involves:
- Targeted recruitment campaigns: Reaching out to diverse talent pools.
- Inclusive workplace policies: Creating an environment where everyone feels welcome and respected.
- Mentorship and sponsorship programs: Supporting career advancement for diverse employees.
By embracing diversity, the automotive industry can tap into a broader talent pool, enriching its workforce and strengthening its ability to adapt to future challenges. This also reflects the diverse customer base the industry serves, leading to more innovative and user-centric product development.
Government Policies and Industry Support
Government plays a pivotal role in supporting workforce development initiatives. Policies that encourage investment in training, provide tax incentives for companies offering apprenticeships, and fund STEM education can significantly impact the industry’s ability to address the skill gap. Collaborative efforts between government and industry are essential for creating a supportive ecosystem.
Industry associations also provide invaluable support by facilitating knowledge sharing, developing industry standards, and advocating for policies that benefit the automotive sector. These organizations often spearhead initiatives to promote careers in manufacturing and connect job seekers with training opportunities. Their collective voice amplifies the needs of the industry.
Funding for Training and Research
Access to funding is critical for implementing large-scale training programs and investing in research and development. Government grants, private sector investments, and public-private partnerships can provide the necessary capital. These funds can be directed towards:
- Developing new training facilities: Equipped with state-of-the-art machinery.
- Subsidizing employee training costs: Making upskilling and reskilling more accessible.
- Funding academic research: Exploring future manufacturing technologies and processes.
Such financial support ensures that manufacturers have the resources to continuously adapt their workforce to the evolving demands of the automotive industry. It’s an investment in the nation’s economic future and global competitiveness.
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Skill Gap Projection | U.S. automotive manufacturers face a projected 8% skill gap by 2025 due to technological advancements. |
| Workforce Development | Companies are investing in upskilling, reskilling, apprenticeships, and certification programs. |
| Industry Partnerships | Collaboration with academia and government is crucial for relevant training and talent pipeline development. |
| Technology Integration | Leveraging AI, automation, and human-robot collaboration enhances efficiency and redefines job roles. |
Frequently Asked Questions About the Automotive Workforce
The skill gap is primarily driven by rapid technological advancements, especially in electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and advanced manufacturing processes like automation and AI. These innovations demand new specialized skills that many current workers and new entrants lack, creating a significant disparity.
Manufacturers are implementing multi-pronged strategies, including extensive upskilling and reskilling programs for existing employees, establishing strong partnerships with educational institutions, and actively promoting STEM education to build a future talent pipeline. They also focus on attracting diverse new talent.
Educational institutions are crucial partners. They are adapting curricula to include new automotive technologies, offering specialized degrees and certifications, and collaborating with manufacturers to ensure graduates possess industry-relevant skills. This collaboration helps align academic offerings with industry demands.
Automation redefines job roles by taking over repetitive tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex, value-added activities. It necessitates new skills in operating, programming, and maintaining advanced robotic systems, fostering human-robot collaboration rather than outright replacement, ultimately enhancing efficiency and safety.
Addressing the skill gap ensures the U.S. automotive industry remains globally competitive, fosters continuous innovation, and supports economic growth. It creates a more resilient, adaptable, and highly skilled workforce capable of navigating future technological shifts, securing the industry’s long-term prosperity and leadership.
Conclusion
The projected 8% skill gap in the U.S. automotive workforce by 2025 is a formidable challenge, yet one that manufacturers are actively and strategically addressing. Through a combination of robust internal training, strong academic and industry partnerships, the smart integration of automation and AI, and proactive talent attraction and retention strategies, the industry is building a resilient and future-ready workforce. These concerted efforts are not merely about filling vacancies; they represent a fundamental commitment to innovation, competitiveness, and the long-term prosperity of the U.S. automotive sector. The future of automotive workforces will undoubtedly be more technologically advanced, collaborative, and dynamic, driven by continuous learning and adaptability.





