Analyzing the Impact of US Regulations on Autonomous Vehicles

Analyzing the impact of new regulations on autonomous vehicle testing and deployment in the US reveals significant challenges and opportunities for manufacturers, tech companies, and consumers, shaping the future of transportation.
The landscape of autonomous vehicle (AV) technology is rapidly evolving, and with it comes a wave of new regulations aimed at ensuring safety and responsible deployment. Analyzing the impact of new regulations on autonomous vehicle testing and deployment in the US is crucial for understanding the future of transportation and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Understanding the Regulatory Framework for Autonomous Vehicles in the US
The United States lacks a unified federal framework for autonomous vehicles, leading to a patchwork of state and local regulations. Navigating this complex landscape requires a thorough understanding of the current rules and how they affect testing and deployment.
Federal Guidance vs. State Laws
At the federal level, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) provides guidance but does not mandate specific regulations. This leaves states to create their own laws, resulting in inconsistencies across the country.
Key Federal Agencies Involved
Several federal agencies, including the Department of Transportation (DOT) and the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), play a role in overseeing different aspects of AV technology, adding to the regulatory complexity.
- NHTSA’s Role: Setting safety standards and issuing voluntary guidelines.
- State Autonomy: States have the primary responsibility for licensing and traffic laws.
- Challenges: Varied regulations can hinder nationwide AV deployment.
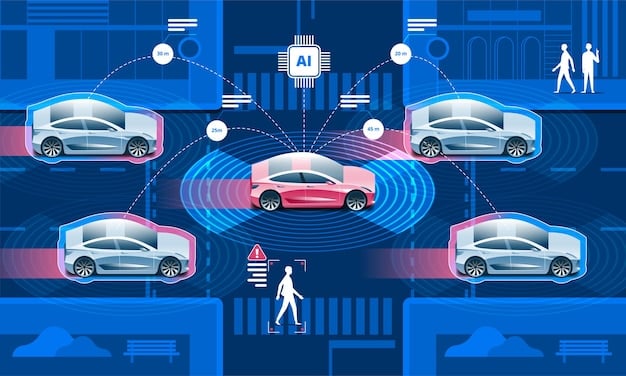
Understanding the interplay between federal guidance and state-level regulations is essential for companies looking to enter the US market. Compliance with these rules is not just a legal requirement but also builds public trust and confidence in AV technology.
The Impact of Safety Standards on AV Testing
Safety standards are at the forefront of autonomous vehicle regulation, influencing how AVs are tested and validated before deployment. These standards aim to prevent accidents and ensure the public’s well-being.
NHTSA’s Safety Assessment Letters
NHTSA encourages manufacturers to submit Safety Assessment Letters, detailing their safety features and testing procedures. Although voluntary, these letters demonstrate a commitment to safety.
Data Collection and Reporting Requirements
Many states require AV operators to collect and report data on vehicle performance, accidents, and near-misses. This data helps regulators understand the risks and improve safety standards.
Stringent testing protocols are necessary to validate the safety of autonomous vehicles before they are released to the public. Virtual simulations, closed-course testing, and real-world trials are all crucial components of this process.
- Virtual Simulations: Testing AV software in a controlled, virtual environment.
- Closed-Course Testing: Evaluating AV performance on designated test tracks.
- Real-World Trials: Gathering data in real-world driving conditions, often with human safety drivers.
Compliance with safety standards requires significant investment in research and development, as well as robust testing infrastructure. Manufacturers must also be prepared to adapt to evolving standards as technology advances.
Data Privacy and Security Regulations
Autonomous vehicles generate vast amounts of data, raising concerns about privacy and security. Regulations in this area aim to protect personal information and prevent unauthorized access to vehicle systems.
Data Collection Practices
AVs collect data on driving behavior, location, and even passenger activities. Regulations may limit the types of data that can be collected and how it can be used.
Cybersecurity Measures
Protecting AVs from cyberattacks is crucial to prevent unauthorized control or data breaches. Regulations may require manufacturers to implement specific cybersecurity measures.
Data privacy and security are paramount in the age of autonomous vehicles. Regulations should strike a balance between protecting individual rights and fostering innovation.
- Data Minimization: Limiting the collection of personal data to what is strictly necessary.
- Transparency: Informing consumers about data collection and usage practices.
- Security Protocols: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect vehicle systems.
Compliance with data privacy and security regulations requires a proactive approach, including data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Manufacturers must also be prepared to respond to data breaches and security incidents.
Insurance and Liability Issues in the AV Era
The introduction of autonomous vehicles raises complex questions about insurance and liability in the event of an accident. Traditional insurance models may need to be adapted to address the unique risks posed by AV technology.
Who is Liable in an AV Accident?
Determining liability in an AV accident can be challenging. Is it the vehicle manufacturer, the software developer, or the owner/operator? Regulations may need to clarify these issues.
Insurance Coverage for AVs
Traditional auto insurance policies may not adequately cover AV-related accidents. New insurance products may be needed to address the specific risks associated with AV technology.
Insurance and liability are critical considerations for the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles. Regulations should provide clarity and ensure that victims of AV accidents are adequately compensated.
- Product Liability: Holding manufacturers liable for defects in AV software or hardware.
- Cyber Liability: Addressing liability for accidents caused by cyberattacks.
- No-Fault Insurance: Streamlining the process of compensating accident victims, regardless of fault.
Addressing insurance and liability issues requires collaboration between regulators, manufacturers, and insurance providers. Clear and comprehensive regulations are essential for fostering trust and confidence in AV technology.
The Impact on Urban Planning and Infrastructure
The deployment of autonomous vehicles has implications for urban planning and infrastructure development. Cities may need to adapt their infrastructure to accommodate AVs and maximize their benefits.
Smart Infrastructure
Connected infrastructure, such as smart traffic lights and sensors, can enhance the performance and safety of AVs. Regulations may encourage or require cities to invest in these technologies.
Changes in Parking Needs
Autonomous vehicles could reduce the need for parking spaces, freeing up valuable urban land. Cities may need to adjust their zoning regulations to reflect these changes.
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to transform urban environments and improve the quality of life for residents. Regulations can play a key role in guiding these changes and ensuring that they benefit all members of the community.
- Traffic Optimization: AVs can communicate with each other to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Accessibility: AVs can provide transportation options for people with disabilities or limited mobility.
- Sustainability: AVs can be designed to be more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Planning for the future of urban mobility requires a holistic approach, considering the social, economic, and environmental impacts of autonomous vehicles. Regulations should be flexible and adaptable to accommodate future innovations.
Ethical Considerations in Autonomous Vehicle Deployment
The deployment of autonomous vehicles raises complex ethical questions, particularly in situations where accidents are unavoidable. How should AVs be programmed to respond in these scenarios?
The Trolley Problem
The trolley problem is a classic thought experiment that explores ethical dilemmas. How should an AV be programmed to choose between different options, each of which results in harm?
Algorithmic Bias
AV algorithms can be biased if they are trained on data that reflects societal biases. Regulations may require manufacturers to address algorithmic bias and ensure fairness.
Ethical considerations are paramount in the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles. Regulations should promote transparency, accountability, and fairness.
- Transparency: Making AV decision-making processes more transparent.
- Accountability: Establishing clear lines of accountability for AV actions.
- Fairness: Ensuring that AV algorithms do not discriminate against any group of people.
Addressing ethical issues requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving ethicists, engineers, and policymakers. Open and inclusive dialogue is essential for shaping ethical guidelines for AV technology.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🚦 Regulatory Framework | US lacks unified federal AV regulations; states set their own rules. |
| 🛡️ Safety Standards | Stringent testing needed: virtual simulations, closed-course, real-world trials. |
| 🔒 Data Privacy | AVs collect a lot of data; regulations aim to protect user information and prevent cyberattacks. |
| ⚖️ Liability Issues | Determining who is liable in AV accidents; new insurance may be needed. |
FAQ
▼
The lack of a unified federal regulatory framework and varying state laws create significant challenges, hindering a consistent approach to AV testing and deployment across the country.
▼
Safety standards mandate rigorous testing protocols, including virtual simulations, closed-course evaluations, and real-world trials, to ensure AVs meet safety benchmarks before public release.
▼
Regulations focus on minimizing data collection, ensuring transparency about data usage, and implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect vehicle systems and personal information.
▼
Liability can fall on the vehicle manufacturer, software developer, or owner/operator, and new insurance products may be necessary to address the unique risks associated with AV technology.
▼
AVs could lead to smart infrastructure development, optimized traffic flow, reduced parking needs, and increased accessibility and sustainability in urban environments.
Conclusion
Analyzing the impact of new regulations on autonomous vehicle testing and deployment in the US highlights the need for clear, consistent, and adaptable rules. Addressing safety, data privacy, liability, urban planning, and ethical concerns is essential for realizing the full potential of AV technology.





